The fight for a new model of search
Since ChatGPT came out, even Google has had to respond to try to contrast the preeminence of this new technology that could kick Google out of the monopoly of search.
ChatGPT-4
The AI chatbot’s updated version is finally here, and it now can produce responses to human inputs by utilizing a wide range of data scraped from various sources, including the internet. The previous version relied on the GPT-3.5 language model, and while it is still accessible, the new and improved version is now offered as part of the ChatGPT Plus package, available for a monthly fee of $20.
Although customers pay a $20 monthly fee, OpenAI can’t guarantee a specific number of prompts from the GPT-4 model per day. Additionally, the maximum number of allowed prompts may change at any time. Although The cap was initially set to 50 messages for four hours, the number may occasionally be lower.
According to Wired, OpenAI states that ChatGPT Plus users have the option of preventing being bumped out of the chatbot during periods of high usage and receiving quicker responses. However, it is important to note that users may have faced difficulties accessing ChatGPT during certain outages. Furthermore, the GPT-4 version currently available might take more time to respond to prompts as compared to GPT-3.5.
Regardless, there are still many unknowns surrounding GPT-4. OpenAI has yet to disclose certain details to the public, such as the size of the model or specific information regarding its training data. However, rumors suggest that the model may contain upwards of 100 trillion parameters.
According to OpenAI, ChatGPT-4 has several new features that allow it to generate more creative and nuanced responses than its predecessor. An example provided by OpenAI was: “Explain the plot of Cinderella in a sentence where each word has to begin with the next letter in the alphabet from A to Z, without repeating any letters”.
ChatGPT-4 answered: “A beautiful Cinderella, dwelling eagerly, finally gains happiness; inspiring jealous kin, love magically nurtures an opulent prince; quietly rescues, slipper triumphs, uniting very wondrously, xenial youth zealously”.
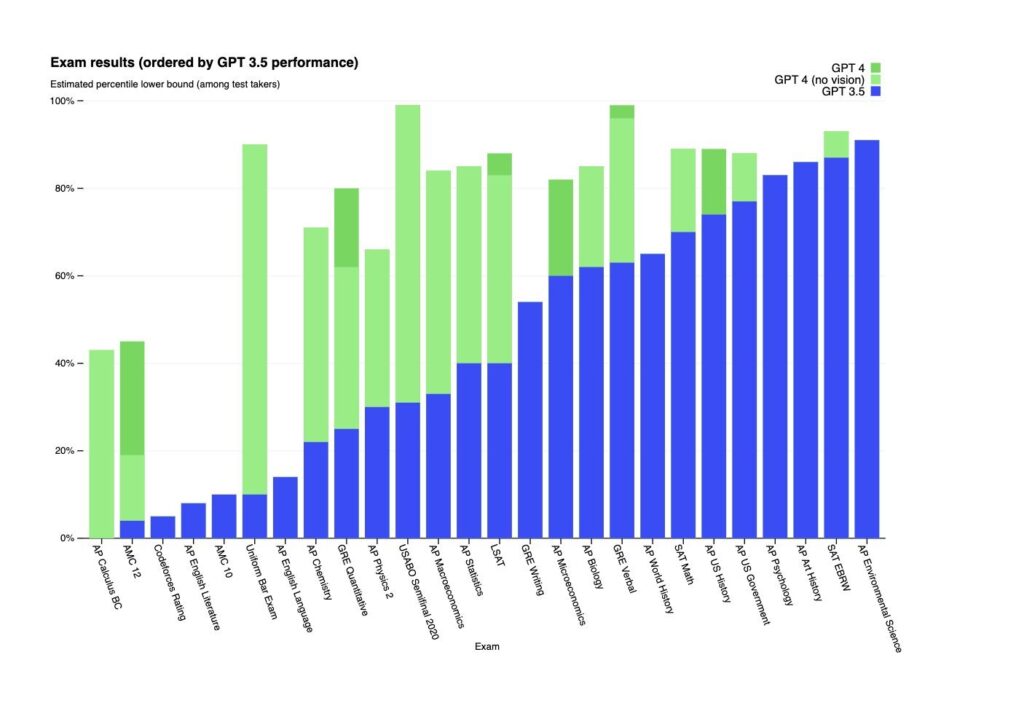
Some of its features include:
Multimodal Capabilities: ChatGPT-4 is designed to process not only text inputs but also images and videos using a “multimodal” approach. Therefore, it can generate and recognize what’s in a picture. And the same could be done with videos and audio, despite we haven’t seen examples yet.
Nonetheless, enrolling in ChatGPT Plus doesn’t currently provide access to the company’s image-analysis capabilities, which have been recently demonstrated.
Greater Steerability: “Steerability” refers to the ability to control the model’s output by providing additional context or constraints. This means users can steer the conversation in a particular direction by providing more specific prompts or instructions. This feature is especially useful in applications that require users to achieve specific goals or results.
Suppose you use ChatGPT-4 to book a flight. Starting by asking, “Can you help me book a flight?” ChatGPT-4 will ask for more information about your travel plans, such as destination and travel date. By providing this information, you can use steerability to specify additional constraints and settings to refine your search. For example, you can say “I want to fly non-stop” or “I want to fly with a particular airline”. ChatGPT-4 uses this information to generate more specific flight options that match your criteria.
Safety: ChatGPT-4 was designed with security in mind and trained on a variety of data to avoid harmful biases.
As the use of AI language models continues to grow, it becomes increasingly important to prioritize safety and ethics in model design. For this reason, OpenAI integrated security reward signals during human-feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF) training to reduce harmful outputs.
Compared to its predecessor, GPT-3.5, GPT-4 has significantly improved security features. This model reduced the tendency to respond to requests for improper content by 82%.
Performance Improvements: ChatGPT-4 handles 8x the words of its predecessor, allowing you to reply with up to 25,000 words instead of the 3,000-word limit of ChatGPT’s free version.
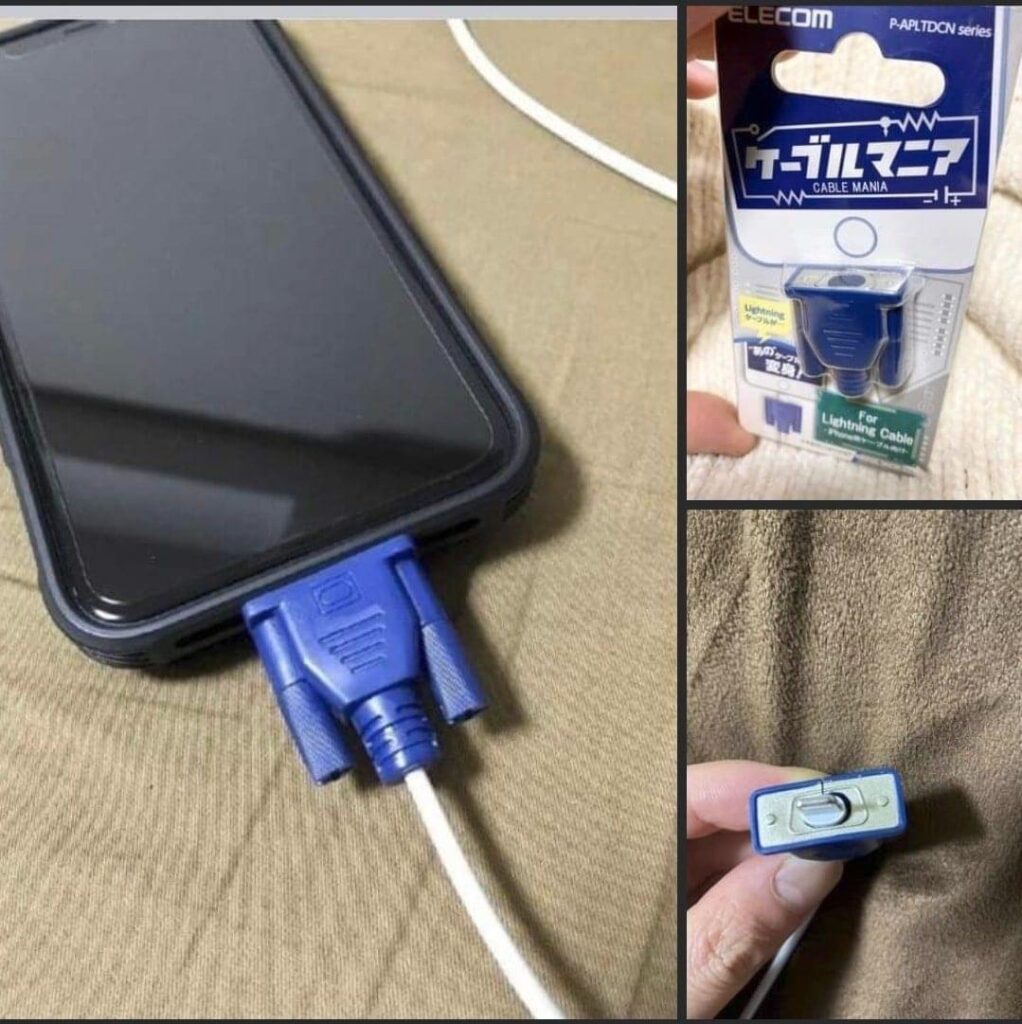

OpenAI also demonstrated ChatGPT-4’s ability to explain why some jokes are funny. The demonstration included a series of images showing the wrong smartphone charger. ChatGPT-4 was able to explain why the situation was humorous. This suggests an ability to understand jokes.
Google Bard
Recently, users are also getting to know Bard, Google’s response to ChatGPT, to see how it stacks up against OpenAI’s chatbot powered by artificial intelligence.
According to this article, it’s a generative AI that responds to questions and performs text-based activities like giving summaries and responses while also producing other kinds of content. By condensing material from the internet and offering links to websites with more information, Bard also helps in the exploration of topics.
After OpenAI’s ChatGPT’s extremely popular debut, which gave the impression that Google was falling behind in technology, Google produced Bard. With the potential to upend the search market and tip the balance of power away from Google search and the lucrative search advertising industry, ChatGPT was seen as a breakthrough technology.
Three weeks following ChatGPT’s debut, on December 21, 2022, the New York Times reported that Google had declared “code red” in order to swiftly respond to the threat posed to its economic model. On February 6, 2023, Google announced the debut of Bard.
Due to a factual error in the demo intended to show off Google’s chatbot AI, the Bard announcement was a shocking failure.
Following this, investors lost faith in Google’s ability to handle the impending AI era, which resulted in Google’s shares losing $100 billion in market value in a single day.
A “lightweight” version of LaMDA, a language model that is trained using online data and information from public dialogues, drives Bard. There are two important aspects of the training:
- A. Safety: By fine-tuning the model using data that was annotated by crowd workers, it reaches a level of safety.
- B. Groundedness: LaMDA grounds its assertions on external knowledge sources (through information retrieval, which is search).
Google evaluated the LaMDA outputs using three metrics:
- Sensibleness: an evaluation of the logicality of a response.
- Specificity: determines whether the response is contextually specific or the exact opposite of general/vague.
- Interestingness: this statistic assesses whether LaMDA’s responses are insightful or stimulating.
Crowdsourced raters evaluated each of the three metrics, and the results were pushed back into the system to keep it improving.
Bard’s potential is currently seen as a search feature. Google’s announcement was vague enough to provide room for interpretation.
This ambiguity contributed to the false impression that Bard would be incorporated into Google search, which it is not. We can state with confidence that Bard is not a brand-new version of Google Search. It is a feature. Bard’s announcement by Google was quite clear: it is not a search engine. This means that while searching leads to solutions, Bard aids users in learning more.
Consider Bard as an interactive way to gain knowledge on a variety of subjects. Large language models have the drawback of mimicking answers, which might result in factual mistakes. According to the scientists who developed LaMDA, methods like expanding the model’s size can aid in its ability to gather more factual data. However, they pointed out that this strategy falters in situations where facts are constantly altering over time, a phenomenon known as the “temporal generalization problem”.
It is impossible to train current information using a static language model. LaMDA uses information retrieval systems as a method of solving the problem. LaMDA examines search engine results since information retrieval systems are search engines.
Question-and-answer datasets, like those made up of questions and responses from Reddit, have the drawback of only representing how Reddit users behave, which makes it difficult to train systems like Bard.
It excludes how others who are not a part of that environment act, the types of questions they might ask, and the appropriate responses to such questions.
After recent tests, users were quite disappointed with Google’s response to OpenAI. Google Bard does not seem to have been as innovative and original as ChatGPT continues to be. Of course, developing a system that takes into account data on the web in an up-to-date way is much more complex than developing a more static dataset. Both in terms of resources and in terms of identifying information. Clearly, these are two different types of searches, though, and we have yet to see how Bard will develop definitively.

